Navigated TMS for clinical use
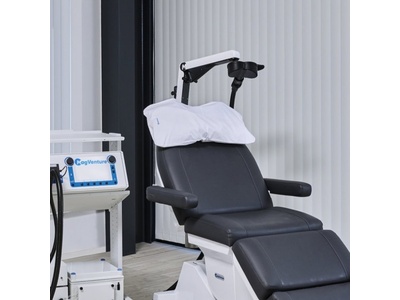
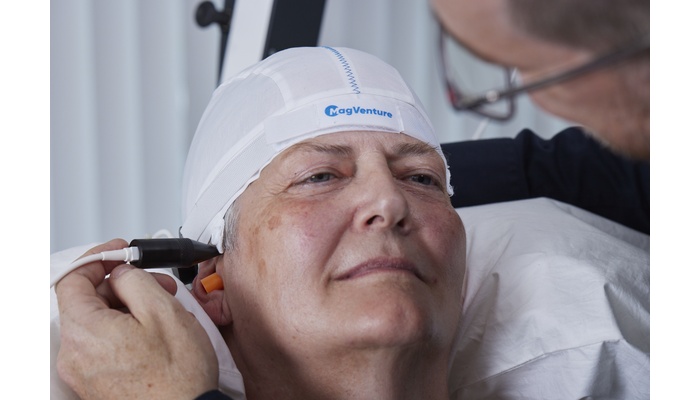
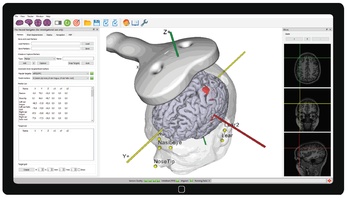
Navigated TMS for clinical use Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) requires accurate and consistent placement of the TMS coil over the targeted brain area to be effective in clinical applications. Conventional placement methods, which rely on external head landmarks like the 10-20 EEG system, often lead to inaccuracies, resulting in suboptimal stimulation and high variability in treatment outcomes. MRI-guided neuronavigation overcomes this problem by aligning a patient's individual MRI scan with their head and providing real-time tracking of both the coil and the patient. This allows the clinician to guide the TMS coil to the intended neuroanatomical structure with millimeter precision, ensuring more precise and consistent delivery of TMS pulses. The use of repetitive TMS (rTMS) with neuronavigation has shown clearly increased efficiency for users and patients alike.
Reproducible coil placement using MNI
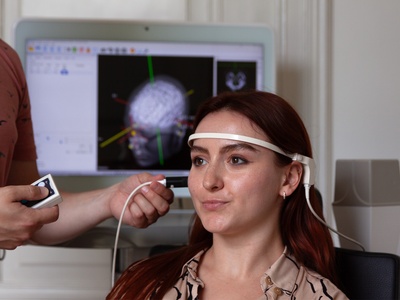
The neural navigator supports accurate reproduction of TMS coil positions using an MNI template. Similar to the standard navigation procedure, facial landmarks of the MNI template are captured on the participant's head. Next, the neural navigator adjusts the MNI template based on the geometry of the participant's head. MNI targets, …
Added value of MRI-guided neuronavigation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) requires accurate placement of the TMS coil over the targeted brain area. Conventional placement methods in TMS are based merely on external landmarks of the head (5 cm rule, 10-20 EEG). This leads to inaccuracies in targeting of this brain area and herewith to suboptimal results …
EM versus optical tracking in neuronavigation
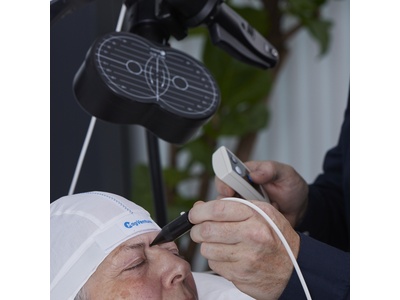
During neuronavigation, the 3D position and angle of the TMS coil, a digitizing stylus and the head of the patient typically must be known at all times. Position tracking can be performed either using optical tracking with large cameras, or electromagnetic (EM) tracking based on a DC pulsed magnetic field …

Treatment of Major Depressive Disorder
MDD, also referred to as clinical depression, is a significant medical condition that can affect many areas of life. MDD is one of the most common mental disorders, 1 out of 6 adults experiences depression. Standard treatment of MDD is medication and psychotherapy. However, about a third of patients with …

Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation in OCD
Obsessive-compulsive disorder (OCD) is a disorder characterized by uncontrollable, recurring thoughts and behaviors. About 2% to 3% of people experience OCD, yet standard treatment such as medicine or exposure therapy achieves (partial) response in only 40% - 60% of the patients. In May 2019 a new treatment was approved by …

Theta burst stimulation (TBS)
rTMS treatment protocols continue to be investigated and improved. New patterned rTMS protocols, where short high frequency trains of TMS pulses are are interleaved with really short breaks, are referred to as Theta Burst Stimulation (TBS), intermittent TBS (iTBS) and continues TBS (cTBS) with frequencies up to 100Hz for the …