Neural Navigator Essentials variant
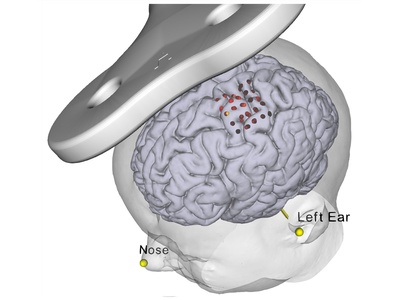
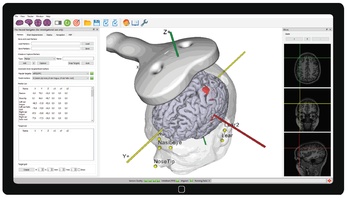
TMS requires accurate placement of the TMS coil over the targeted brain area. Conventional placement methods in TMS are based merely on external landmarks of the head (e.g 5 cm rule). This leads to inaccuracies in targeting of this brain area. To overcome this problem, an individualized MRI scan of the subject can be used to accurately guide the TMS coil to the specific brain target in order to correct for differences in the shape and the size of that specific brain (MRI- guided neuronavigation). Our Neural Navigator "Essentials" uses electromagnetic tracking for neuronavigation with an accuracy of at least 4mm and herewith efficient TMS stimulation of targeted brain regions is assured. The software offers an easy workflow for uploading an individual MRI image, performing brain segmentation, and creating stimulation targets in the brain. The system is compatible with many brands of TMS machines such as Neurosoft, MagStim, and Magventure. The Neural Navigator is CE certified as a medical device in the EU and FDA cleared for clinical use in the USA.

Regulatory
- The Neural Navigator is CE certified as a class IIa medical device in the European Union and FDA cleared in the USA, Furthermore, it is InMetro and ANVISA certified in Brazil, Health Canada certified and TGA certified in Australia. In these regions the Neural Navigator can be used for clinical purposes.
- The Neural Navigator as an electrical medical device is compliant with IEC 606011 3rd edition (Electrical Safety) and IEC 60601-1-2 3rd edition (electromagnetic compatibility) as well as RoHS and WEEE.
Components
- The BrainTRAK position tracker with 4 tracking sensors and magnetic field transmitter.
- Plastic hand-held pointer for measuring facial landmarks and a remote control for navigation.
- A sturdy suitcase with compartments fitting all components, allowing easy and safe transportation and storage
- A reclining comfortable TMS treatment chair.
Features & performance
- Precision: The Neural Navigator can target brain areas indicated on an individual MRI scan with a precision of at least 4 mm (Neggers et al, 2004).
- Tracking technology: electromagnetic tracking using highly robust DC pulsed EM tracking (often used in neurosurgical neuronavigation). The precision of the tracking is at least 1mm.
- MRI scans needed: straightforward T1 weighted MRI scan at around 1mm cubic resolution.
- Formats supported: DICOM import/export, Nifti import/export. fMRI and DTI results from SPM/FSL/AFNI are readable.
- Built in robust semi-automatic MRI scan segmentation.
- Supports fMRI activation overlays and targeting.
- Actual 3D coil models for most Neurosoft coils built into the software.
Reproducible coil placement using MNI
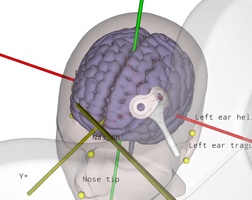
The neural navigator supports accurate reproduction of TMS coil positions using an MNI template. Similar to the standard navigation procedure, facial landmarks of the MNI template are captured on the participant's head. Next, the neural navigator adjusts the MNI template based on the geometry of the participant's head. MNI targets, …
Added value of MRI-guided neuronavigation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) requires accurate placement of the TMS coil over the targeted brain area. Conventional placement methods in TMS are based merely on external landmarks of the head (5 cm rule, 10-20 EEG). This leads to inaccuracies in targeting of this brain area and herewith to suboptimal results …
EM versus optical tracking in neuronavigation
During neuronavigation, the 3D position and angle of the TMS coil, a digitizing stylus and the head of the patient typically must be known at all times. Position tracking can be performed either using optical tracking with large cameras, or electromagnetic (EM) tracking based on a DC pulsed magnetic field …