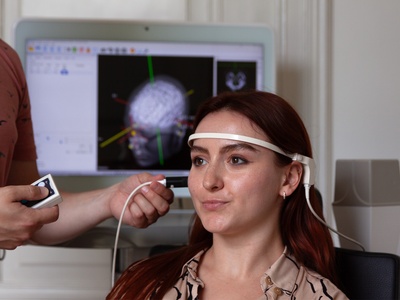
Navigated TMS for research
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) is a popular non-invasive brain stimulation method that is increasingly used in brain research by neuroscientists. TMS can be used to interfere with functions such as memory, motor control, perception, attention and other cognitive functions during task performance in order to investigate the neural underpinnings of these functions. By adding an MRI-guided neuronavigation system to a TMS device, the exact location of a TMS pulse can be visualized on the brain surface with millimeter precision. Using these techniques, causal brain-behavior relationships can be studied, and brain functions accurately mapped. Additionally, researchers are using MRI-guided neuronavigation and paired pulse TMS to study the motor cortex of the brain, as well as cerebral, spinal and peripheral pathways, and the connectivity of the brain. We offer complete TMS solutions targeted at such brain research applications, and offer assistance and advice for your own special requirements.

Reproducible coil placement using MNI
The neural navigator supports accurate reproduction of TMS coil positions using an MNI template. Similar to the standard navigation procedure, facial landmarks of the MNI template are captured on the participant's head. Next, the neural navigator adjusts the MNI template based on the geometry of the participant's head. MNI targets, …
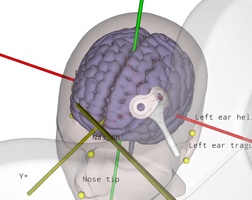
Added value of MRI-guided neuronavigation
Transcranial Magnetic Stimulation (TMS) requires accurate placement of the TMS coil over the targeted brain area. Conventional placement methods in TMS are based merely on external landmarks of the head (5 cm rule, 10-20 EEG). This leads to inaccuracies in targeting of this brain area and herewith to suboptimal results …
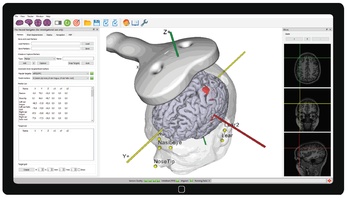
EM versus optical tracking in neuronavigation
During neuronavigation, the 3D position and angle of the TMS coil, a digitizing stylus and the head of the patient typically must be known at all times. Position tracking can be performed either using optical tracking with large cameras, or electromagnetic (EM) tracking based on a DC pulsed magnetic field …