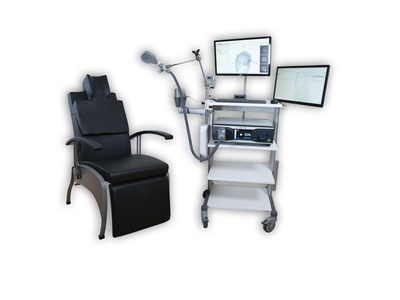
Neural Navigator MotorMap variant
Transcranial magnetic stimulation induces electrical currents in the brain non-invasively, which excite nerve cells and consequently produces action potentials. A motor evoked potential (MEP) can be registered if an electromyography (EMG) is recorded at the moment of stimulation. The Neural Navigator “Mapping” variant can exactly determine where the TMS coil evokes the strongest field, and visualize the MEP properties of each stimulation location on the brain surface. That way, maps of muscle-controlling brain regions in the motor cortex can be created of up to 8 muscles at a time (i.e. for each stimulus). With the use of this approach cerebral, spinal and peripheral pathways can be studied. Such tests are especially important for studying patients with brain damage after stroke or surgical procedures, or suffering from demyelinating diseases of the nervous system. This navigator variant requires a Neurosoft EMG unit. It is a co-development of Neurosoft and Brain Science Tools BV, and integration is seamless. This solution is cleared by the FDA for general purpose motor mapping in clinical use in the USA , CE certified for clinical use in the EU, and cleared for clinical use in Australia and Brazil.

Components
- The Neural Navigator software suite "MotorMap"
- A reclining comfortable TMS treatment chair.
- The BrainTRAK neuronavigation position tracker with 4 tracking sensors and magnetic field transmitter.
- Plastic hand-held pointer for measuring facial landmarks and a remote control for navigation.
- A sturdy suitcase with compartments fitting all navigator components, allowing easy and safe transportation and storage
- Technical and user manuals
- All required cabling
- Note: The Neural Navigator MotorMap variant functions best with TMS and EMG systems of Neurosoft. The MotorMap complete solution offers a complete setup of the Neural Navigator MotorMap variant, the Neurosoft Neuro-MS/D monophasic TMS unit, and the Neuro-MEP-micro 2-channel ultraportable EMG and NCS system.
Features & performance
- Precision: The Neural Navigator can target brain areas indicated on an MRI scan with a precision of at least 4 mm (Neggers et al, 2004).
- Tracking technology: electromagnetic tracking using highly robust DC pulsed EM tracking (a technique often used in neurosurgical neuronavigation). Precision better than 1mm.
- MRI scans needed: straightforward T1 weighted MRI scan at around 1mm cubic resolution.
- Formats supported: DICOM, Nifti. Also supports fMRI activation overlays and targeting.
- Built in robust semi-automatic MRI scan segmentation.
- Visualizes stimulation locations and evoked MEP amplitude or latency
- MEPs can be filtered, thresholded and manipulated in many other ways, and saved to disk to be loaded at a later time point for inspection or further analysis in martlab, python, etc.
- Actual 3D coil models for most Neurosoft coils built into the software.
Regulatory
- The Neural Navigator is CE certified as a class IIa medical device in the European Union and FDA cleared in the USA, Furthermore, it is InMetro and ANVISA certified in Brazil, Health Canada certified and TGA certified in Australia. In these regions the Neural Navigator can be used for clinical purposes.
- The Neural Navigator as an electrical medical device is compliant with IEC 606011 3rd edition (Electrical Safety) and IEC 60601-1-2 3rd edition (electromagnetic compatibility) as well as RoHS and WEEE.
Reproducible coil placement using MNI
The neural navigator supports accurate reproduction of TMS coil positions using an MNI template. Similar to the standard navigation procedure, facial landmarks of the MNI template are captured on the participant's head. Next, the neural navigator adjusts the MNI template based on the geometry of the participant's head. MNI targets, …
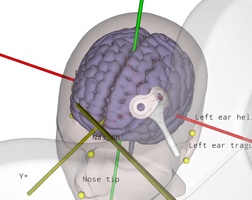
TMS motor mapping in stroke
Transcranial magnetic stimulation (TMS) can be used to non-invasively induce a current and generate neuronal activity within the primary motor cortex. The neuronal activation travels through the corticospinal tract and the peripheral nervous system to finally elicit activity in various muscles, depending on the exact location of stimulation. The electrical …

EM versus optical tracking in neuronavigation
During neuronavigation, the 3D position and angle of the TMS coil, a digitizing stylus and the head of the patient typically must be known at all times. Position tracking can be performed either using optical tracking with large cameras, or electromagnetic (EM) tracking based on a DC pulsed magnetic field …